Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion (boilers, water heaters, generators, vehicles, charcoal). It reduces oxygen delivery in the body and can be fatal. This guide explains CO ppm safe levels, provides practical charts, and tells you exactly what to do at common readings.
Safety note:
If your CO alarm sounds or you suspect exposure, get to fresh air immediately and call local emergency services. Troubleshoot later.
CO Exposure Limits
CO Alarm Behavior
Symptoms by PPM
What to Do if CO is High
Common CO Sources
Prevention Checklist
FAQ
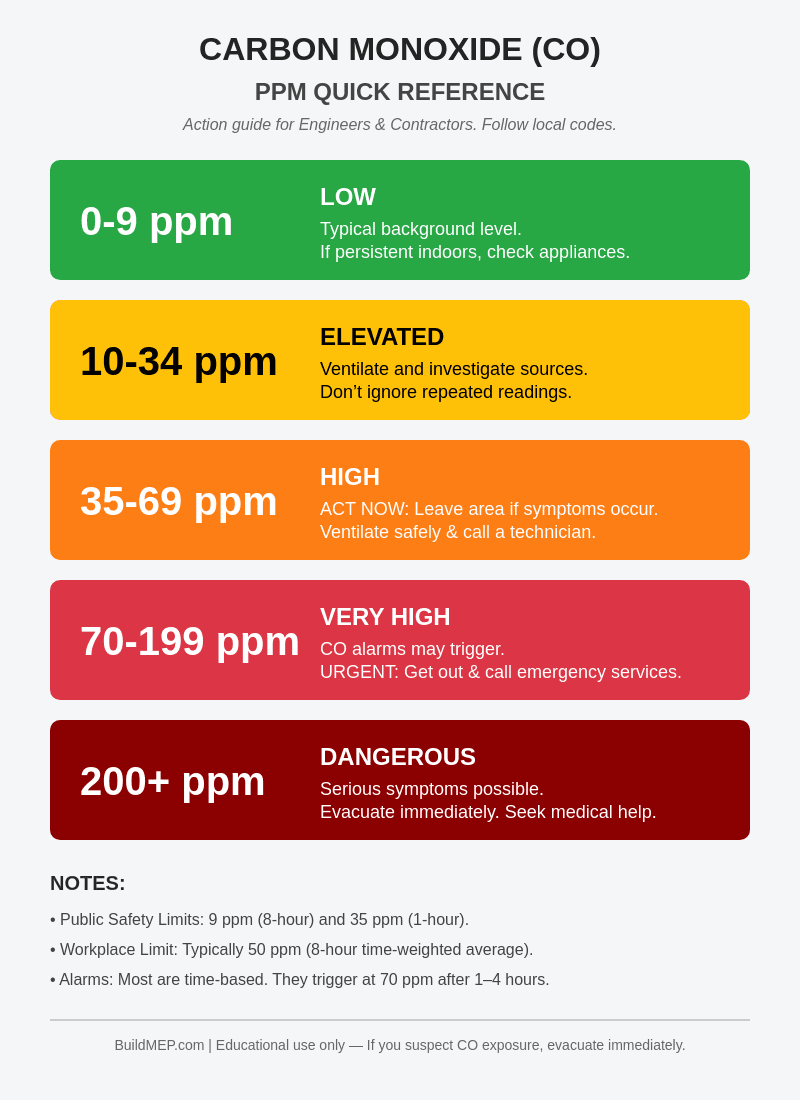
CO PPM Levels at a Glance
- 0–9 ppm (Low): Typical background. Investigate appliances/ventilation if persistent.
- 10–34 ppm (Elevated): Ventilate and investigate source. Repeated readings are a red flag.
- 35–69 ppm (High): Leave area if symptoms; ventilate; call technician.
- 70–199 ppm (Very High): Treat as urgent. Many alarms trigger here over time.
- 200+ ppm (Dangerous): Evacuate immediately; seek medical help if symptoms occur.
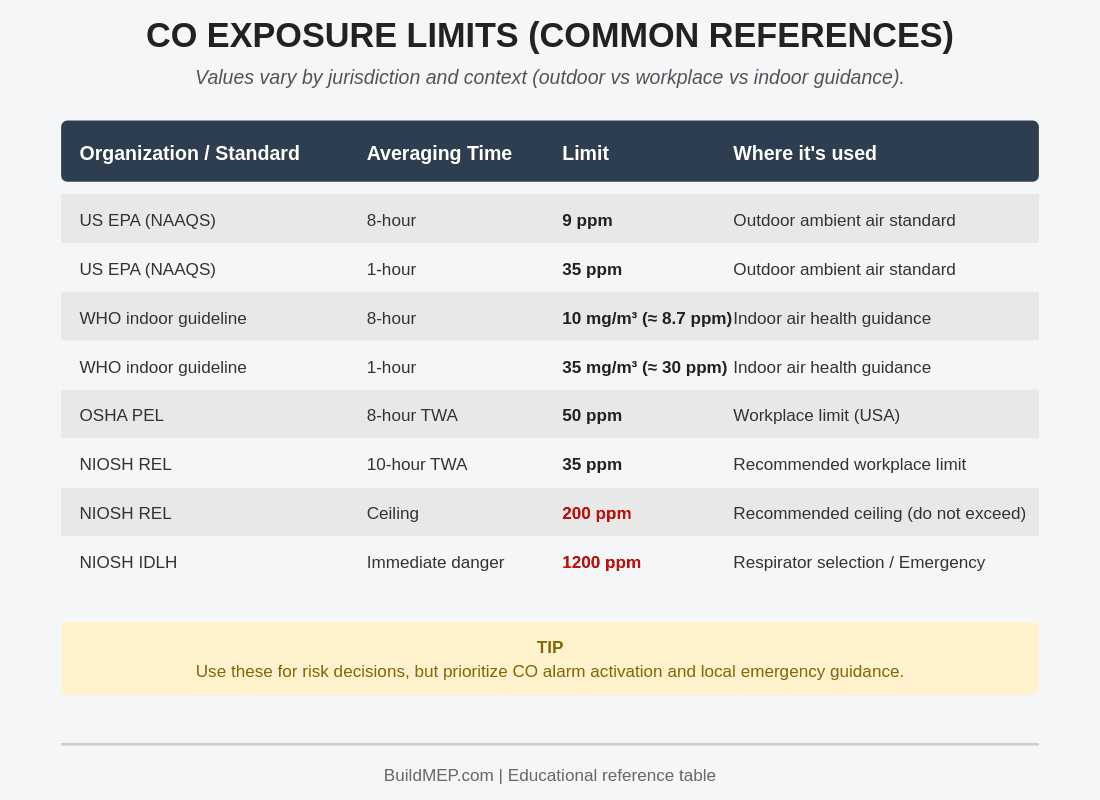
CO Exposure Limits
Public Health Reference (EPA)
- 9 ppm (8-hour average)
- 35 ppm (1-hour average)
WHO Indoor Air Guidelines
- 10 mg/m³ for 8 hours (~8.7 ppm)
- 35 mg/m³ for 1 hour (~30 ppm)
- 100 mg/m³ for 15 minutes (~87 ppm)
Occupational Limits
- OSHA PEL: 50 ppm (8-hour TWA)
- NIOSH REL: 35 ppm TWA, 200 ppm ceiling, 1200 ppm IDLH
CO Alarm Behavior
Many residential CO alarms reduce nuisance alarms by responding to exposure over time. Dangerous levels may exist before the alarm sounds.
Tip: Treat any confirmed CO reading as urgent even if the alarm hasn’t sounded.
Symptoms by PPM
CO poisoning often feels like the flu. Common symptoms include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, chest pain, confusion.
- ~200 ppm: headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea after a few hours
- ~400 ppm: strong headache in 1–2 hours; life-threatening if exposure continues
What to Do if CO is High
- Evacuate immediately
- Call emergency services
- Account for everyone (children, elderly, pets)
- Do not re-enter until cleared
- Fix the source (appliance service, venting)

Common CO Sources
- Cracked heat exchanger (furnace)
- Backdrafting water heater
- Blocked chimney/flue
- Generators near windows/doors
- Vehicle exhaust in garages
- Charcoal grills / shisha indoors
- Poor combustion from burners
Prevention Checklist
- Install CO alarms near sleeping areas & each level
- Service fuel-burning appliances annually
- Ensure proper combustion air & venting
- Never run generators indoors / near windows
- Do not idle vehicles in garages
- Check kitchen exhaust/backdrafting issues
BuildMEP Tip: Integrate CO sensors into BMS for proper ventilation and monitoring.
FAQ
What CO ppm is considered safe?
Common references: 9 ppm (8-hr) and 35 ppm (1-hr). Persistent indoor readings require investigation.
Is 10 ppm dangerous?
Typically elevated. Ventilate and investigate if persistent indoors.
When does a CO alarm go off?
Alarms respond to dose over time. Evacuate immediately if symptomatic.
OSHA CO limit?
50 ppm TWA (8-hour).
Symptoms of CO poisoning?
Headache, dizziness, nausea, weakness, chest pain, confusion. Move to fresh air and seek help.